Machines can tirelessly analyze data day and night, continuously discovering patterns in numerous human scenarios: credit card fraud alerts, spam email detection, stock price forecasting, personalized product and video recommendations, and more. They are becoming increasingly intelligent in these tasks. This is known as “Analytical AI” or “Traditional AI”.However, humans excel not only in analyzing things but also in creativity. We write poetry, design products, create games, and write code. Until 2022, machines did not have the opportunity to compete with humans in creative work; they could only engage in analytical and rote cognitive labor. But now machines have begun to surpass humans in the field of creating emotional and beautiful things, and this new category is called “Generative AI”.
Generative AI will not only become faster and cheaper but in some cases, it will outperform human-created works. Every industry that requires human creativity – from social media to gaming, from advertising to architecture, from coding to graphic design, from product design to law, from marketing to sales – is poised for a complete transformation. Some functions may be completely replaced by generative AI, or they may inspire entirely new ideas beyond human imagination.
If knowledge structures like TCP/IP and HTML were the foundations of the previous era, when facing the ongoing AI era, each of us should perhaps ask ourselves a question: “What is the knowledge foundation of the AI era?” Perhaps this knowledge foundation will be the Transformer.
Transformer and Attention Model:
In the past five years, the world of artificial intelligence has undergone significant and exciting changes. Many of these changes have been driven by a paper titled “Attention is All You Need.” Published in 2017, this paper introduced a new architecture called the “Transformer.” The following diagram illustrates the architecture of the Transformer model as described in the “Attention is All You Need” paper:
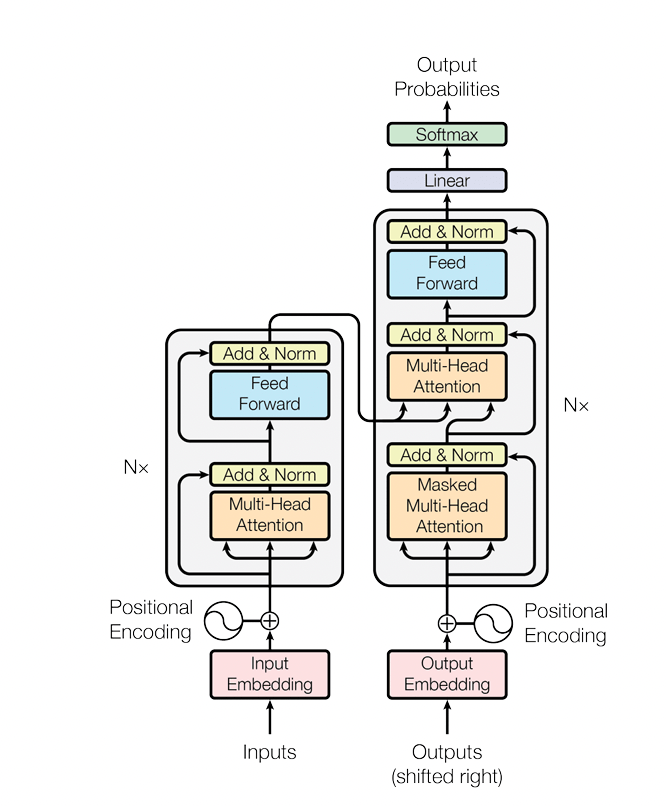
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf?trk=cndc-detail
In summary, the Transformer model has made two significant contributions to the field of machine learning. Firstly, it improved the efficiency of using parallel computation in artificial intelligence. Secondly, it introduced the concept of “attention,” which allows AI systems to understand the relationships between words. The evolution of the Transformer architecture has led to advancements in various domains, such as GPT-3, BERT, Sable Diffusion, and more.
The attention mechanism is a technique in artificial neural networks that mimics cognitive attention. This mechanism enhances the weights of certain parts of the input data while reducing the weights of other parts, thereby focusing the network’s attention on the most important subset of the data. Which parts of the data are deemed more important than others depends on the context. The attention mechanism can be trained using gradient descent.
The flexibility of the attention mechanism stems from its “soft weighting” characteristic, which means that these weights can be dynamically changed at runtime, unlike typical weights that are typically fixed during runtime. The Transformer model utilizes multi-headed attention, which involves parallel computation of a specific attention function known as scaled dot-product attention. The diagram below illustrates this process:
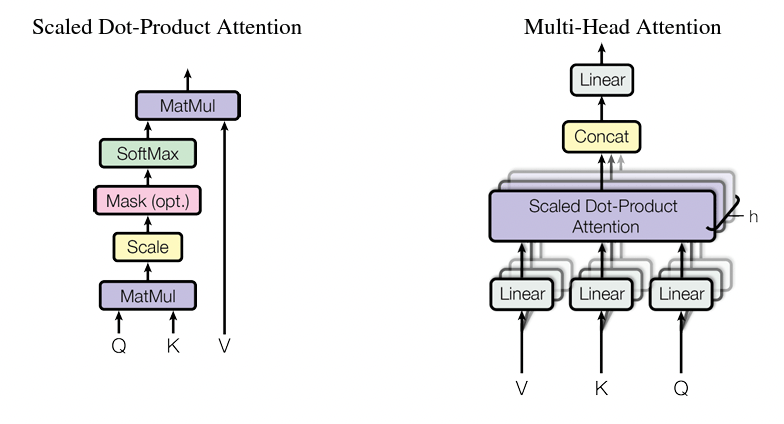
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf?trk=cndc-detail
Economic potential of generative AI
McKinsey conducted an analysis surveying 47 countries, 850 occupations, 63 application examples, and over 2,100 detailed job activities, covering approximately 80% of the global workforce. According to McKinsey, the rapid global growth and influence of generative AI products such as ChatGPT, Midjourney, Bard, Claude, and Stable Diffusion can be attributed to their simplicity and user-friendly text-based dialogue, making them accessible to almost everyone. These AI products find applications in various tasks, including writing marketing copy and generating videos, images, and music. Notably, ChatGPT has played a crucial role, surpassing the capabilities of any previous generative AI product.
McKinsey believes that with the widespread adoption of generative AI, industries such as high technology, banking, retail and consumer packaged goods, healthcare, and advanced manufacturing will experience the greatest impact, generating approximately $1 trillion in economic benefits annually. The impact of generative AI on productivity could add trillions of dollars in value to the global economy. Among the 63 use cases analyzed by McKinsey, generative AI has the potential to contribute $2.6 to $4.4 trillion in annual economic revenue.
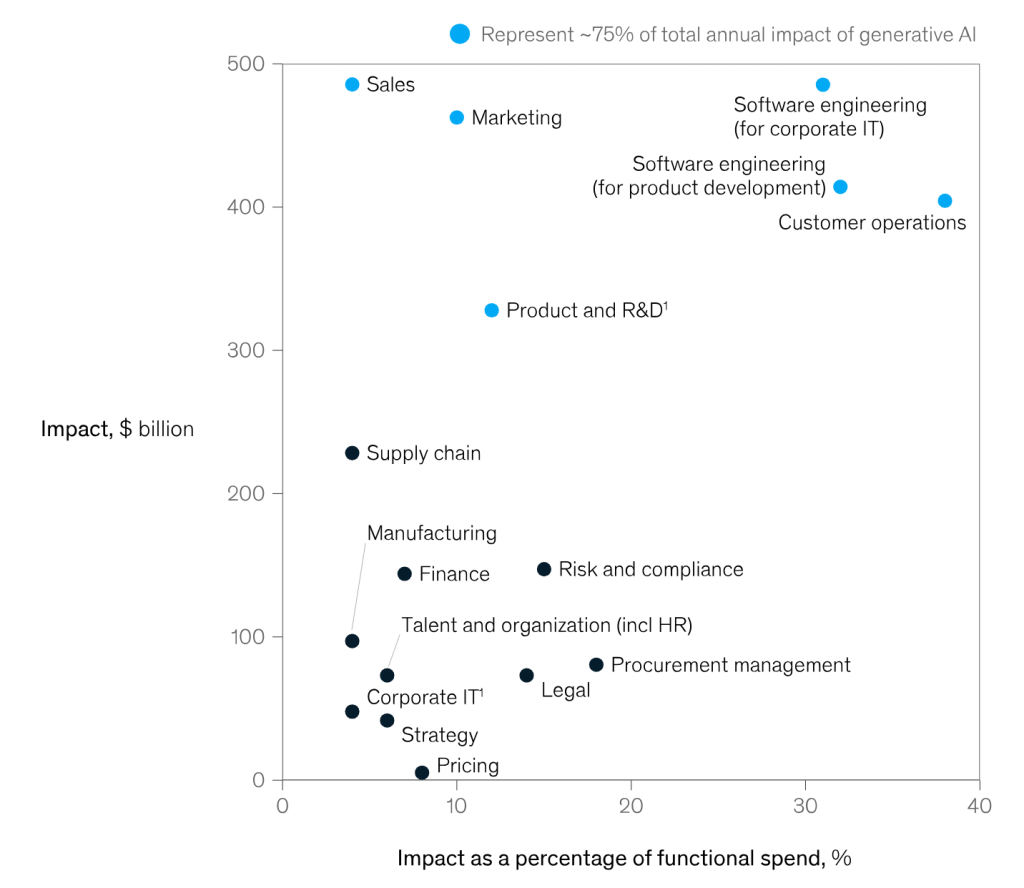
Approximately 75% of the economic value provided by generative AI is distributed across four domains: customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and product development. McKinsey analyzed 63 use cases across 16 business scenarios, where generative AI can address various specific business needs, such as automatically generating marketing and sales creative content based on text prompts or generating computer code.
Generative AI will impact all industries, with high technology, banking, retail and consumer packaged goods, healthcare, and advanced manufacturing being the most affected. For instance, in the banking sector, leveraging generative AI to its full potential could create an additional $200 to $340 billion in economic value annually. Retail and consumer packaged goods will also experience significant impact, generating $400 to $600 billion in economic benefits each year. Given the potential for increased business process automation with generative AI, the pace of workforce transformation may accelerate. McKinsey estimates that by 2030 to 2060, half of the current jobs could be automated, possibly achieving this as early as 2045.
Generative AI has the potential to significantly enhance labor productivity across the entire economy, but it requires investment to support worker transitions and job switching. By 2040, generative AI could contribute to an annual labor productivity growth rate of 0.1% to 0.6%, depending on the adoption rate of the technology and the speed at which workers can be redeployed to other tasks. When combined with all other technologies, work automation can increase productivity by 0.2% to 3.3% annually.
The era of generative AI is just beginning. The enthusiasm for this technology is evident across various industries, and early business pilots have shown promising results. However, to fully unleash its maximum potential, business and societal leaders still face significant challenges. These include managing the inherent risks of generative AI, determining the new skills and capabilities employees will need, and reimagining core business processes such as retraining and developing new skills.
Among the 63 use cases analyzed by McKinsey, high technology, banking, retail and consumer packaged goods, healthcare, and advanced manufacturing emerge as the industries most impacted by generative AI:
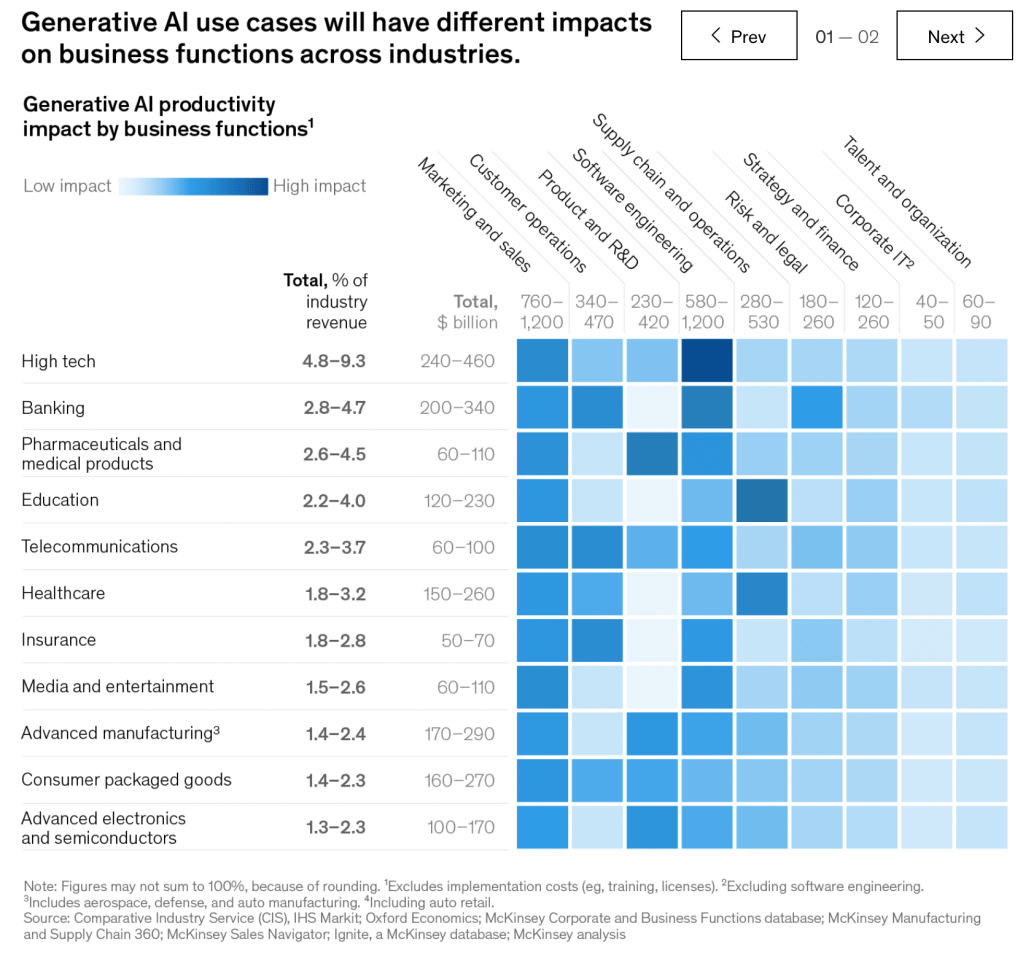
Generative AI could have an impact on most business functions; however, a few stand out when measured by the technology’s impact as a share of functional cost:
Leave a comment